Wireless Review
Quiz
You Scored:
Ranking:
You Scored:
Ranking:
You Scored:
Ranking:
Diagram
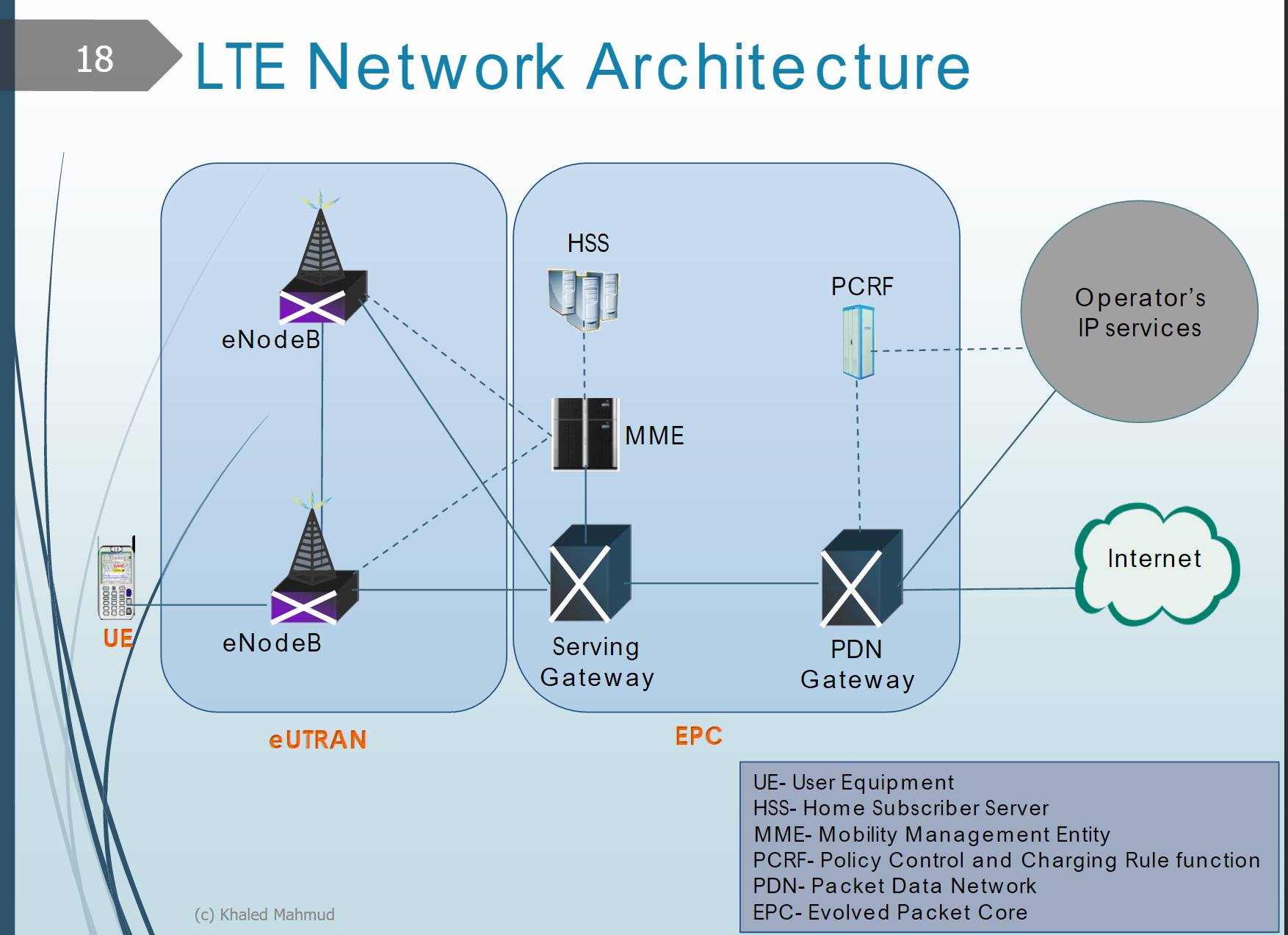
LTE

CSMA/CA
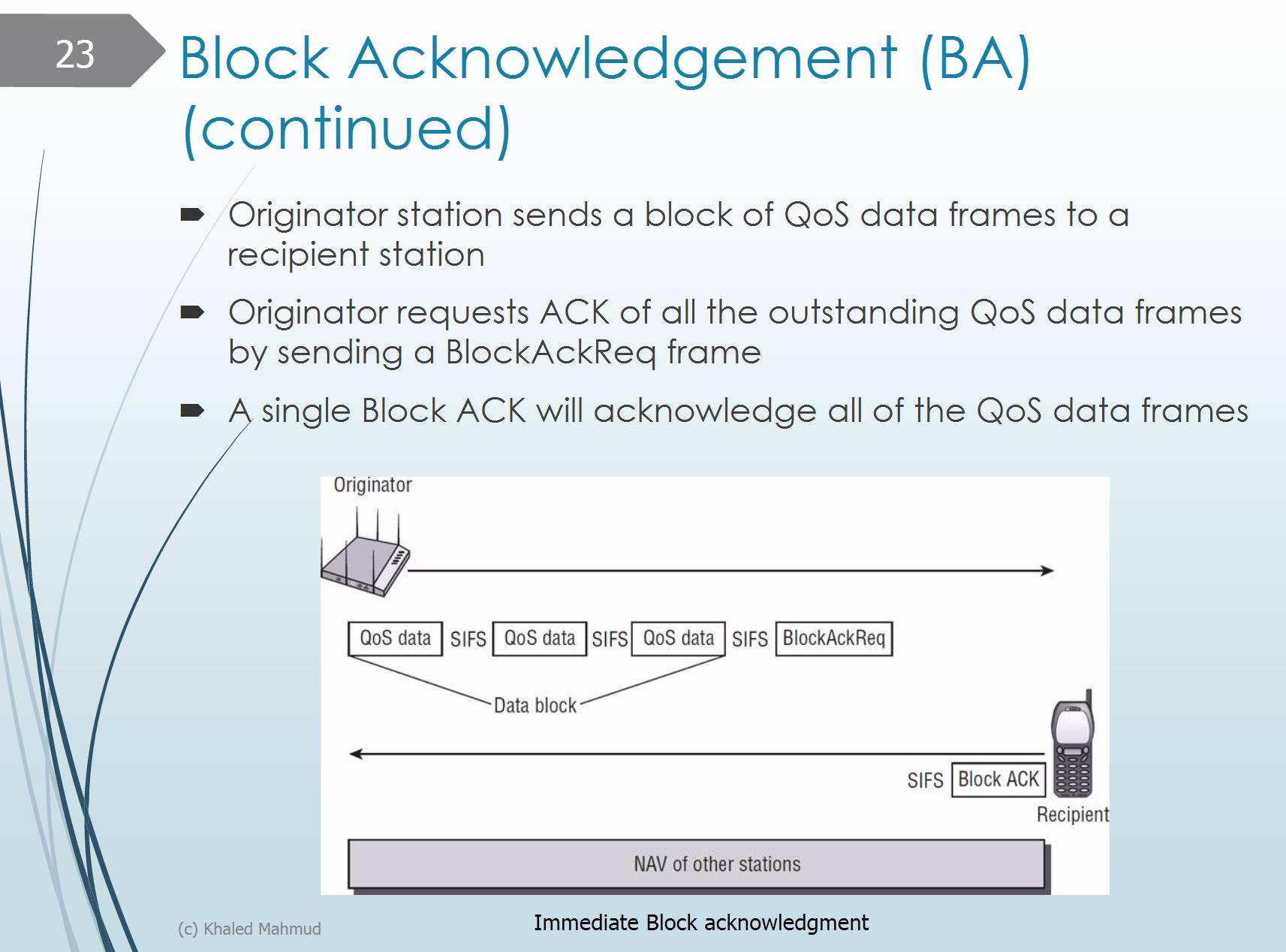
Immediate Block Acknowledgement
Cellular System Question
Chapter 1
-
Which algorithm is used to digitize a voice signal for transmission in a digital circuit-switched network and at which datarate is the voice signal transmitted?
-
Name the most important components of the GSM Network Subsystem (NSS) and their tasks.
-
Name the most important components of the GSM radio network (BSS) and their tasks.
-
How is a BTS able to communicate with several subscribers at the same time?
-
Which steps are necessary to digitize a speech signal in a mobile device before it can be sent over the GSM air interface?
-
What is a handover and which network components are involved?
-
How is the current location of a subscriber determined for a mobile-terminated call and how is the call forwarded through the network?
-
How is a subscriber authenticated in the GSM network? Why is an authentication necessary?
-
How is an SMS message exchanged between two subscribers?
-
Which tasks are performed by the RISC processor and which tasks are performed by the DSP in a mobile device?
-
How are data stored on the SIM card?
-
What is CAMEL and for which services can it be used?
Chapter 2
-
What are the differences between circuit-switched and packet-switched data transmission?
-
What are the advantages of the data transmission over GPRS compared to GSM?
-
Why are different modulation and coding schemes used?
-
What is the difference between the GPRS ready state and the GPRS standby state?
-
Does the GPRS network perform a handover if a cell change is required while data is transferred?
-
Which are the new network elements that have been introduced with GPRS and what are their responsibilities?
-
What is a temporary block flow?
-
What actions are performed during an inter-SGSN routing area update (IRAU)?
-
Why is IP used twice in the protocol stack of the Gn interface?
-
Why is it not necessary to change any settings on the mobile device for GPRS when roaming abroad?
-
What is the difference between a GPRS attach and a PDP context activation?
-
Why is an Access Point Name (APN) necessary for the PDP context activation procedure?
-
How are MMS messages sent and received via GPRS?
-
Name the different parts of an MMS message
Chapter 3
-
What are the main differences between the GSM and UMTS radio network?
-
What advantages does the UMTS radio network have compared to previous technologies for users and network operators?
-
What were the datarates for a packet-switched connection that were offered by early Release 99 UMTS networks?
-
What does OVSF mean?
-
Why is a scrambling code used in addition to the spreading code?
-
What does ‘cell breathing’ mean?
-
What are the differences between the Cell-DCH and the Cell-FACH RRC states?
-
In which RRC states can a mobile device be in PMM connected mode?
-
How is a UMTS soft handover performed and what are the advantages and disadvantages?
-
What is an SRNS relocation?
-
How is the mobility of a user managed in Cell-FACH state?
-
What is the compressed mode used for?
-
What are the basic HSDPA concepts to increase the user datarate?
-
How is a circuit-switched voice connection handled during an ongoing HSDPA session?
-
What are the advantages of the Enhanced-DCH (E-DCH) concept?
-
Which options does the Node-B have to schedule the uplink traffic of different E-DCH mobile devices in a cell?
Chapter 4
-
How many subcarriers are used for a 10-MHz FDD LTE channel?
-
What is the difference between an S1 and an X2 handover?
-
Describe the differences between the tasks for the MME and the tasks of the Serving Gateway.
-
What is a resource block (RB)?
-
How does a mobile device get access to the Physical Uplink Shared Channel?
-
What are the differences between ARQ and HARQ?
-
What is the difference between a default and a dedicated bearer?
-
What is the purpose of DRX in RRC Connected state?
-
How is mobility controlled in RRC Idle state?
-
What is the difference between a Cell Change Order and a Handover?
-
How can the LTE core network be interconnected with legacy core networks and why should this be done?
-
What is CS fallback?
-
What is the big disadvantage of Internet-based voice services compared to network operator-based voice services?
-
Describe different options for the backhaul connection of the eNode-B.